Increase in understanding of the welding process through simulation of laser beam and gas-shielded metal arc welding
Authors: Dr.-Ing. Oleg Mokrov, Dipl.-Phys. Marek Simon, M. Sc. Rahul Sharma, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Uwe Reisgen, M. Sc. Christoph Schöler, Dr. rer. nat. Markus Nießen, Prof. Dr. rer. nat. habil. Wolfgang Schulz
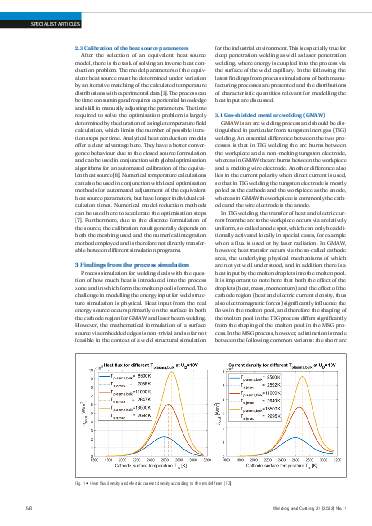
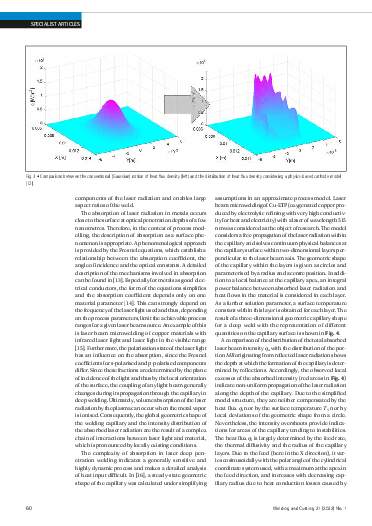
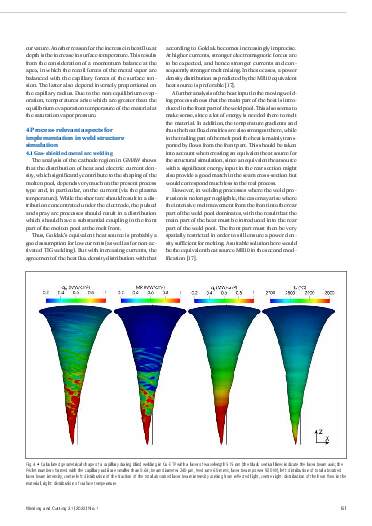
In welding structure simulation, the thermal effect of welding in the component is represented by an equivalent heat source. In order to be able to capture phenomena such as grain growth and structural transformation in the structure simulation, in addition to the amount of heat input, its distribution on mesoscopic, spatial scales must also be specified. With known approaches for the equivalent heat source, the physical process is still not sufficiently understood, and an exact calibration is very complex. With the aim of finding more accurate equivalent heat sources for the consideration of mesoscale phenomena, this work analyses laser beam and gasshielded metal arc welding (GMAW) in selected areas of the process parameters and discusses process properties that should be taken into account when formulating the heat source. These include formation of welding capillary in laser deep welding, which is significantly influenced by the absorption properties of the metallic material surface, as well as the distribution of heat flow and electrical current density on the cathode in the GMAW process, which are significantly influenced by evaporation.
An active subscription enables you to download articles or entire issues as PDF-files. If you already are a subscriber, please login. More information about the subscription